Private Sector Participation:
Consequent on opening up of the defence industry sector in May 2001, allowing Indian private sector participation with FDI cap of 26%, a number of JVs have mushroomed between Indian and foreign companies.
| Editor’s Pick |
Major private sector industries and SMEs are actively engaged in software development, engineering services, manufacturing & sub assemblies, accounting for 17% of outsourcing18 to DPSUs, OFs.
They are also associated with national & strategic programmes like LCA, MBT (Main Battle Tank), Pinaka, Arihant, Dhanush & Brahmos.
Many of them have excellent facilities like Tatas, L&T, Pipava but significant limitation in terms of design capability and system’s integration.
The Buy & Make (Indian) option in 2009 would provide private sector a window to TOT19 which was the exclusive preserve of DPSUs/OFs earlier.
 They are now into cost effective production of fast patrol vessels and IPVs & outcompeting defence shipyards – thanks to the level playing field provided in Ship Building Procedure.20 Even DPSUs like HAL are giving way to the Tatas in manufacture of Aerostructures & Cabins where foreign OEMs like Lockheed Martin & Sikorsky have shown distinct predelection for partnership with Tatas
They are now into cost effective production of fast patrol vessels and IPVs & outcompeting defence shipyards – thanks to the level playing field provided in Ship Building Procedure.20 Even DPSUs like HAL are giving way to the Tatas in manufacture of Aerostructures & Cabins where foreign OEMs like Lockheed Martin & Sikorsky have shown distinct predelection for partnership with Tatas
3. Self Reliance
Self-Reliance Index was defined as the ratio of Indigenous Systems Procurement Cost to Total System Procurement Cost of the year.22
Despite the impressive indigenous capability, Self Reliance Quotient has not moved beyond 30% since 1993.
In the aerospace sector, predominant reliance on licensed manufacturing without taking adequate steps to bolster nascent design and development capability is a major cause,23 of our lack of indigenous capability in the fighters segment.
The most serious problem in aircraft design, development and production is the vertical disjunction between design, development and production agencies.24
The Soviet Union brought the production agencies directly under the design bureau with remarkable results. Tony Saich also observes that the major orgnisational problem with S&T System has been lack of linkage across vertical structure; particularly between research & production sectiors.25
The Defence Expenditure Review Committee (2009) accordingly makes a strong case for drawing a self reliance road map for attaining the goal of 70% indigenisation in a 15 – 20 year time frame.26
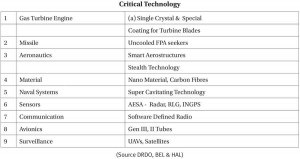
4. Gaps in Critical Areas of Technology
Self-Reliance is linked to indigenous capability to design, develop & produce critical subsystems like Propulsion, weapon, sensors of major platforms. The areas identified by Dr. Kalam 18 yrs’ back remain largely unchanged Even aerograde material used for fuselage by fighters27 and high quality steel required by frigates, submarines and aircraft carrier,28 our dependence on imports is around 90%. It is sometimes alluded to lack of economies of scale29 which is indefensible as India must have indigenous capability to produce such critical material to meet recurring requirement for aircraft and naval platforms.
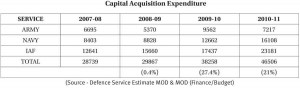
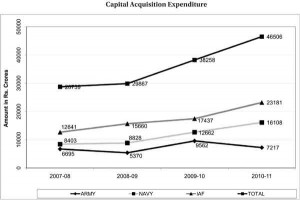
5. Budget Trends: Capital Acquisition
There has been a significant spurt in acquisition by IAF and Navy in recent years, major acquisition contracts signed being viz. MIG 29 (upgrade) (Rs.3856 Cr.), Medium Lift Helicopters (Rs.5600 Cr), C-130 J aircraft (Rs. 366 Crores) and LRMRASW (Long Range Maritime Reconnaissance and Surveillance) Aircraft) for the Navy (Rs.10684 Crores).
The trend of capital acquisition expenditure is placed below:
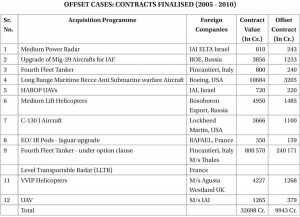
5. Offset Contracts (2005-2010)
The broad details of the 12 acquisition programmes & offset contracts concluded with foreign companies is placed below:-
Continued…: Impact of Offset Policy on India’s Military Industrial Capability – II