
Image Courtesy: https://www.stopkillerrobots.org/act/
Lethal Autonomous Weapons Systems (LAWS) are highly sophisticated autonomous military weapon systems with an array of sensor suites and pre-programmed computer algorithms which can independently search, select, designate, track, engage and eliminate hostile targets. These weapon systems, once activated can destroy targets without further human intervention.
Hence LAWS on a broad scale can transform the structure of war by bringing in Artificial Intelligence (AI) into systems governing weapons where humans would remain out of the loop. Currently AI-triggered Revolution in Military Affairs (RMA) is happening in the leading military establishments across the world.
Legality and Ethical Concerns
LAWS, often dubbed as “killer robots” can be ethically challenged view lethality and machines replacing humans in taking critical tactical decisions. Owning responsibility for a misfire is the main hurdle in deployment and commissioning of LAWS.
LAWS raise a host of philosophical, psychological and legal issues since it is a killer machine having AI embedded with no human control. In fact, these weapons have the potential to disrupt the present conventional way of fighting war. Human rights activists are up in arms to ban LAWS, as they would violate the International Humanitarian Laws (IHL) under the Geneva Convention and International Human Rights Law (IHRL) under Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR).
The unrest among employees of Google involved in the prestigious ‘Project Maven’ of Pentagon shows the growing awareness on LAWS among youngsters. ‘Project Maven’ is an AI based project sponsored by DAPRA, which studies the imagery of battle prone area that would eventually improve the strike capability of drones in the battle prone area.
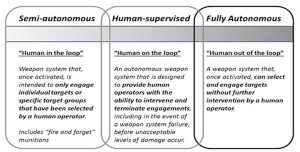
Evolution and Classification of LAWS
LAWS are evolved over a period of time along with AI. The autonomous elements have increased gradually to reach a point where humans have no role to take a decision whether to engage a target or not. LAWS have been evolved or classified into three different categories as shown below. The one in contention is the fully autonomous one where humans are not in the loop while engaging a weapon.
Current Status of Deployment
Fully-autonomous defensive systems have already been deployed by many advanced countries to intercept enemy air aggression. Defensive weapon systems are deployed to seek all incoming aerial targets. The most common autonomous defensive weaponry is the Missile Defence Systems (MDS).
Both US and Israel have deployed and tested MDS successfully. Fire-and-forget systems have been deployed by both UK and Israel. Even South Korea uses the SGR-A1, a sentry robot with an automatic mode, in the Demilitarised border zone with North Korea.
Norway’s has an offensive autonomous system which will be deployed under the Joint Strike Missile program of NATO. This system can hunt, recognize and detect a target ship or land-based object without human intervention. Both Russia and China are developing similar systems at a faster pace.
Role of AI
AI has become a very competitive emerging technology. AI would become the centre of the global power play triggering a second cold war. The reality today is that AI is leading us towards an algorithmic battleground which has no boundaries or borders and wars will be fought without human involvement. It will be impossible to understand and control this ecosystem in cyberspace and geo-space domain.
Machine learning and deep learning would facilitate effective deployment of AI. New generation GPUs and high-speed hardware with large memorycapacity can accelerate the computing speed and perform big data analysis and very high-speed communication.
United Nations and LAWS
Efforts to regulate LAWs have again ended in a stalemate at UN in November 2019. Dialogue happened at UN to address the ramifications of LAWS on human rights.28 governments demanded a blanket ban on artificial intelligence weapons. But both the US and Russia blocked the move and recommended to form legally binding agreements.
During the meeting, member countries of Convention on Conventional Weapons (CCW) could not come in common grounds for a resolution against LAWS. But they have decided to continue the talks for regulating lethal autonomous weapons systems in the next two years. UN diplomats expressed disappointment and blamed Russia for watering down the agenda. Unsatisfied with the lack of progress in the CCW, NGOs have started Campaigning against LAWS, urging countries to bypass the UN convention and to negotiate a separate treaty.
In the recently concluded Paris Peace Forum, UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres again called for a new international treaty to ban LAWs. He stated that “the machines that have the power and discretion to kill without human intervention are politically unacceptable and morally despicable”.
Challenges in Cyber Security
The need for a scalable, automated, high-speed vulnerability detection and patching system is growing to make cyber controlled weapons safe. More and more military platforms are getting connected through internet backbone. Embedded software-controlled machines are audited to find the flawed code and vulnerability and correspondingly patches are applied against potential hacking prior deployment.
AI/Machine learning (ML) can take up the challenge of automation process of identifying vulnerabilities and simultaneously patching it in the cyber domain. It can simultaneously exploit the vulnerabilities of enemy systems redefining the next level of cyber warfare.
There are numerous ways we can increase the autonomy for interaction between conventional and virtual. Cyber operations can be used as a tool to increase the autonomy in conventional weapon systems as well as in countermeasure operations. We can trigger unintended interactions and emergent behaviours between autonomous systems. If not firewalled adequately, autonomous weapon systems will remain vulnerable to cyber operations.
LAWS – India’s Stand
Countries like Russia, China, US, and Israel are spending billions of dollars in the AI research. Artificial intelligence has the potential to transform the combat capabilities of Armed Forces. AI Leadership can always give nations a military edge over adversaries. Amidst calls for a ban on LAWS, India is planning to strengthen their AI-based weapon systems.
The recommendation was made by the 17-member newly formed AI task force under Ministry of Defence, which includes members from research organisations, contractors and the military recommends India to enhance AI towards better operational readiness of armed force.
The task force has identified few use cases to start with which includes unmanned tanks, under water vessels, aerial vehicles and robotic weaponry. Since India is in nascent stage of development, it is too early to speak about LAWS now.
Conclusion
With the current pace at which the AI being integrated to Military Systems, days are not far where the war machines could become vulnerable and might go out of human control. UN and Human right organisation are sensing this danger and is all out to stop this disaster. Nations will go into a self-destruction mode if they integrate AI into Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD).
LAWS are dangerous systems, once engaged, would trigger counter and counter operations without human interventions. In a nut shell we will live in a world where lethal machines will fight with each other for their respective masters and these masters can seldom control them.
There is an imminent requirement to monitor and control the development of LAWS by UN to save the humanity and India has a larger role to play in making LAWS safe.
Sources
• https://www.militaryaerospace.com/computers/article/
• https://breakingdefense.com/2019/10/artificial-intelligence -will-detect-hidden-targets-in-2020-wargame/
• https://breakingdefense.com/2018/11/army-ai-task-force -comes-to-pittsburgh-c-o-cmu/
• https://sonix.ai/articles/difference-between-artificial- intelligence-machine-learning-and-natural-language-processing/
• https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/artificial- intelligence-military-operations-where-does-india-stand-54030/
• https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market- Reports/artificial-intelligence-military-market-41793495.html
• https://usiofindia.org/publication/usi-journal/artificial -intelligence-in-military-operations-technology-and-ethics-indian-perspective/
• https://thebulletin.org/2018/04/the-promise-and-peril -of-military-applications-of-artificial-intelligence/
• https://analyticsindiamag.com/indias-plan-on-laws- showcases-that-it-wants-to-play-a-bigger-role-in-the-ai-arms-race/





While the article is thought provoking, I am unsure with the author’s opinion on this subject. Is LAWS good or bad, and from the information above, like any other deterrent, despite UN recommendations, countries are proceeding in this direction.. need to wait and watch the outcome