Shivalik is the first ship of the Project 17 Frigates designed by the Indian Navy and built by Mazagon Docks Limited Mumbai. This project was conceived to incorporate stealth features and in the process other state of the art systems are also introduced in a modern indigenous warship. The Navy has succeeded in design and building of such a sophisticated class of warship with indigenous efforts duly supported by industry and select international agencies. The success of this project and the novel features built into the design of Project 17 Frigates are briefly highlighted in this articles.
 The stealth features make it difficult for the enemy to locate this ship and the detection ranges have been considerably reduced. The modern payload judiciously selected for this class of warship adds to the lethal punch of the growing blue water capability of the Navy. The combined diesel or gas – CODOG main propulsion system provides simplicity and reliability in operations, gives higher endurance ranges and is most economical in fuel consumption. This will result in as low as one-third operating costs compared to combined gas or gas – COGOG system. The savings may be over Rs 2000 crores over the lifecycle of the warship.The lines of the ship and the form parameters have been so evolved by the designers to give the best hydrodynamic and sea keeping, manoeuvrability and handling characteristics. Even on high speeds, there is no roll, no pitch, no vibrations and the ship has turned out to be ideal, stable naval platform for naval warfare. The propellers have been specially designed for cavitation inception speeds of over 22 knots and qualify to be quiet and silent propellers.
The stealth features make it difficult for the enemy to locate this ship and the detection ranges have been considerably reduced. The modern payload judiciously selected for this class of warship adds to the lethal punch of the growing blue water capability of the Navy. The combined diesel or gas – CODOG main propulsion system provides simplicity and reliability in operations, gives higher endurance ranges and is most economical in fuel consumption. This will result in as low as one-third operating costs compared to combined gas or gas – COGOG system. The savings may be over Rs 2000 crores over the lifecycle of the warship.The lines of the ship and the form parameters have been so evolved by the designers to give the best hydrodynamic and sea keeping, manoeuvrability and handling characteristics. Even on high speeds, there is no roll, no pitch, no vibrations and the ship has turned out to be ideal, stable naval platform for naval warfare. The propellers have been specially designed for cavitation inception speeds of over 22 knots and qualify to be quiet and silent propellers.
For enhancing the warfare capability, the warship incorporates new generation technology through an indigenous system called the AISDN (ATM based integrated ship borne data network) that allows electronic information from ship’s sensors and systems to be transmitted digitally in real time over the common data base. ATM has been seen as the ultimate networking technology that will allow the true broadband working for the future. The warship incorporates advanced survivability features through robust structure, ample watertight sections and fire zones.
Habitability is considerably improved through modular accommodation totally air conditioned. The concept of Total Atmospheric Control (TAC) has been adopted where all the air intake is through the Air Filteration Units (AFUs) and the TACs controls temperature and humidity of air coming into the ship at all times. This warship caters for women officers serving on board.
Stealth Features
The primary aim of stealth is to reduce platform susceptibility, increase survivability and therefore prevent damage and reduce demands on defensive systems. Low signatures make the detection of the ship more difficult and give it more time to react. The important signature are Radar Cross Section (RCS), Radiated Noise, and Infra Red (IR).
Radar Cross Section
The Radar Cross Section (RCS) is entirely determined by the shape and material properties of the ‘above water part’ of the ship’s hull, superstructure and sensor fit. RCS of a target is its ability to capture incident EM energy and radiate back towards radar. RCS is reduced by hull-shaping, to avoid vertical surfaces and avoid corner reflectors. Radar transparent materials have been used for manufacture of guard rail stanchions and helicopter grid frames. RCS screens have been provided for the boats. Several computer programmes are available for prediction of radar signatures, which serve as an effective tool for comparison of various options and evolving a good stealth ship design. RCS reduction and prediction are generally performed in frequency range 2 – 40 GHZs.
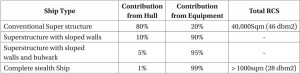
The following table shows the comparison of typical RCS values of a conventional ship with vertical surfaces and the kind of reductions possible by simple shaping and concealment of weapons, exposed deck fittings and equipment:-
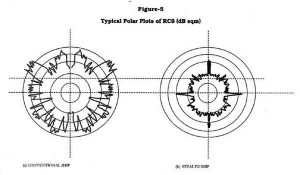
A good balance between contribution from bare hull and weapon/equipment is required to evolve an overall stealth design. A typical RCS polar plot for a stealth ship is given in figure-5.
Infra Red Signatures
The principal sources of infra red – IR signature are the plume and hot parts of the stacks. Work on the IR signatures concentrates on the reduction of exhaust gas temperatures and cooling of visible exhaust ducting.
The electro magnetic radiation emitted by the ship from the above sources in the two infra red band widths; 3-5m (medium infra red) band and 8-12 FIR (far Infra red) band is used in designing the IR sensors to detect the ship. The IR signature of the engine exhaust can be reduced by approximately 95 percent in the 3-5m band by a plume cooling device. The IRSS device “Eductor Diffuser” system has been used for the main machinery.