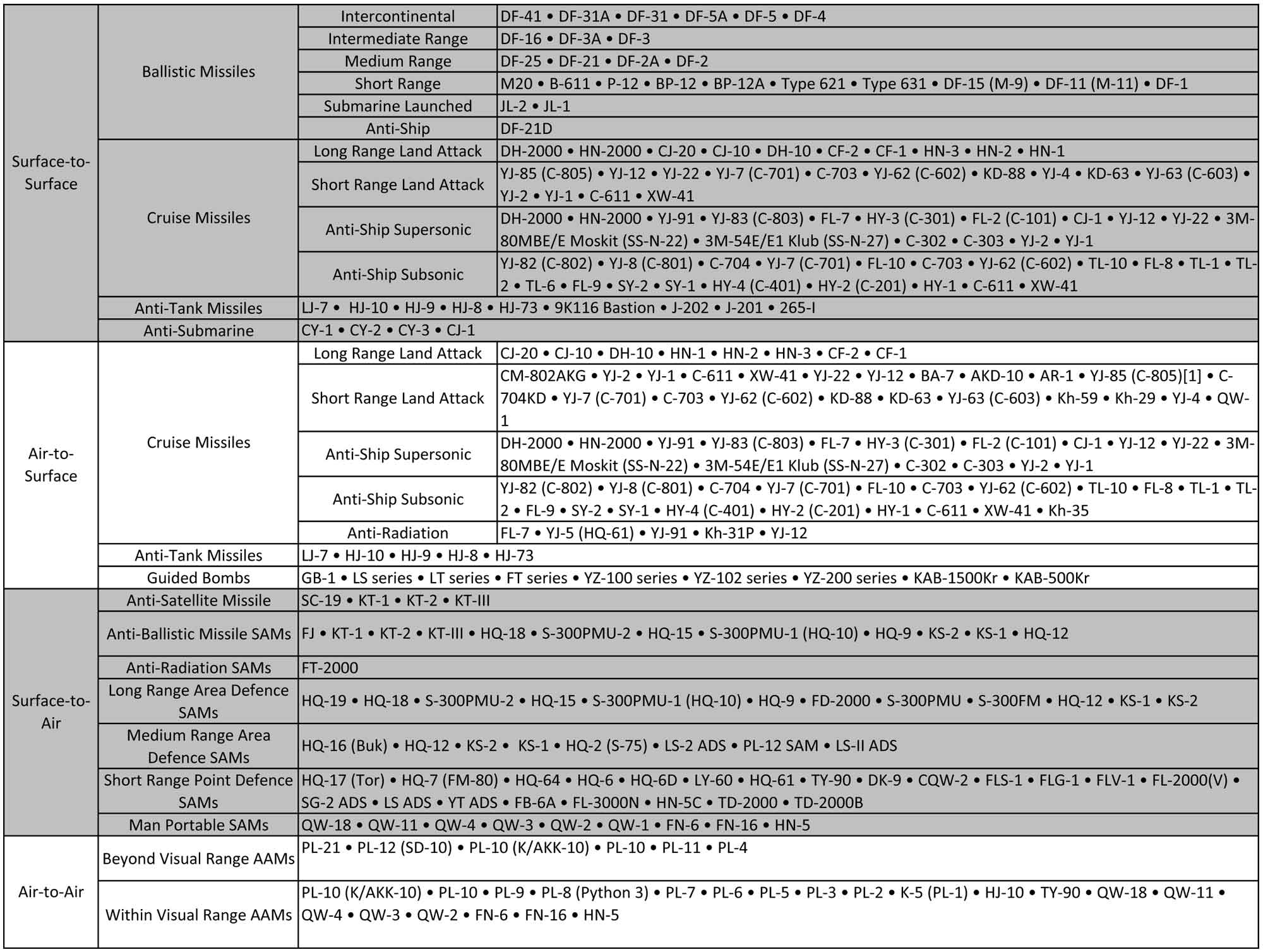
Founded in 1966, the PLA’s dedicated missile force was named the Second Artillery Corps by former Premier Zhou En Lai. It has been an independent branch of the PLA since 1974 and controls the day-to-day operation of nuclear and non-nuclear long, intermediate and short range ballistic missiles. The Second Artillery fired its first long-range DF-5 ICBM in May 1980 into the Pacific Ocean near Tarawa. While the Second Artillery is an independent branch, it does not have the same status as the Army, Air Force and Navy. It is subordinate to the General Staff of the PLA, but it is believed that it reports directly to the Central Military Commission (CMC).
The Second Artillery Headquarters is located in Qinghe, near Beijing. During peacetime, the headquarters performs administrative, planning and budgetary functions. It is designed and mandated to shift during wartime. One report holds that use of nuclear weapons would be a collective decision of the Standing Committee of the Politburo and the CMC. Command of conventional missiles, however, would shift to the wartime national command in Beijing, which would be in direct contact with a temporary theater level, or “war zone”, that would group missiles under its command into a Theatre Missile Corps. Missile strikes would be co-ordinated with air, naval, army, artillery, electronic warfare and special forces operations.
The PLAs new long-range ballistic missiles use modern liquid and solid fuel motors. Early ICBM like the DF-5, and early IRBMs like the DF-4 and DF-3, used storable liquid fuels.
The Second Artillery is reported to have a strength about 90,000 personnel. Some estimates reckon it to be 120,000. There are eight Base Headquarters. Each Division or Base is commanded by a Major General. Divisions have departments for political, communication, logistic, training and nuclear warhead maintenance purposes.
A division comprises brigades which is the basic missile-firing unit of the Second Artillery. The number of brigades have grown from 19 to 22. More are likely to be formed to control missiles aimed at Taiwan. Brigades are commanded by a Senior Colonel. Mobile brigades are further divided into battalions, comprising ‘launch companies’. A ‘launch company’ has a launch vehicle, an electrical generation vehicle, survey and communications vehicles, and a missile transporter/re-supply vehicles.
Missile brigades are divided between nuclear and conventional units. Mobile nuclear brigades include those equipped with the DF-31 ICBM, DF-4 IRBM, DF-21 IRBM and the DF-3 IRBM. In the future DF-21 brigades could contain non-nuclear warhead armed missiles. Non-nuclear missile brigades would include those armed with the DF-15 SRBM and the DF-11 SRBM. It is expected that the Second Artillery and the Army will in the future receive ground-launched mobile land-attack cruise missile units. Their structure would possibly be akin to the SRBM brigades, except that the ‘launch vehicles’ are most likely to launch multiple missiles.
Missile Related Modernisation
The PRC’s ongoing modernisation of its ballistic missiles and cruise missiles is made possible by technical advances in areas of engines, guidance and warheads. In many cases the PRC is also able to incorporate foreign technology, that it has either purchased, stolen, or obtained clandestinely. Ballistic missile development is largely co-ordinated by the First Academy of the China Aerospace Technical Corporation (CATC).
It is the largest research and development organisation with about 27,000 personnel on its rolls.
Engines
The PLA’s new long-range ballistic missiles use modern liquid and solid fuel motors. Early ICBM like the DF-5, and early IRBMs like the DF-4 and DF-3, used storable liquid fuels. Such fuels are highly corrosive if kept in the missile, so, they have to be loaded into missile fuel tanks just before launch. But, when this is done in the open the missile becomes vulnerable to counterstrikes. Like the DF-3 IRBM is said to require about 2-3 hours to prepare for launch. However, the PLA has decided to continue with the use of liquid-fueled motors, in that, it is replacing early DF-5 ICBMs with an upgraded modified version.
Guidance
The accuracy of new intercontinental, intermediate and short range ballistic missiles has been given added impetus by the development of improved guidance system. The primary guidance system for older DF-5 ICBMs, and newer Mobile ICBMs is the inertial guidance system based on internal gyros.
Smaller Warheads
Critical to the success of the PLA’s new long range missiles has been the development of a new class of smaller nuclear warheads that confer greater accuracy and allow for multiple warhead carriage. The DF-5 ICBM carries a single large 3-5 megaton nuclear warhead that weighs about 3,000 kgs. This is too large for modern Mobile ICBMs. The DF-5 warhead, most likely, has a blunt, semi-circular shape, meaning it is not capable of high accuracy.
…Moscow continues to sell arms to China is a difficult question to answer, but money alone cannot be the reason. Certainly the entire Russian Pacific coast, including Vladivostok, is placed at ever increasing risk by these new Chinese capabilities.
The successful development of new mobile and solid fueled ICBMs by the PRC also include development of new smaller nuclear warheads. As noted earlier, these warheads are believed to weigh about 500 kg to 700 kg, and feature modern payload design, as also modern, sharp and more accurate conical shapes.
Multiple Warhead System
In Jul, 2002 the US Department of Defence revealed that to enhance the penetration chances for its missile warheads, the PLA undertook a number of measures, including–“perhaps (the) development of a multiple warhead system for an ICBM, most likely for the CSS-4 (DF-5)”. This may mean that the new DF-5 Mod 2 may carry a MIRV bus. The PRC is said to have developed multiple independent targetable re-entry vehicle (MIRV) warhead technology since long.





MCM satchel 2013 submit c be communicated up and summer a tidy advertising
MCM, all products are made ??using the finest materials, workmanship, purses using only the most advanced materials, leather is condition, unwavering, waterproof and can stand up to UV rays, MCM medley was founded in 1976 in Munich, Germany, is the builder of Hollywood superstar – Michael Cromer, the letters “MCM” role Manner, Beginning, Munich. MCM business rating throw in the towel lines to clothing, ready rags and leather-based. MCM earliest started to bring up leather goods, in the 1980s, the stamp’s heyday, MCM forming, including jewelery, watches, perfumes, clothing, bags and immature leather goods, etc., more than five hundred models of the product. It is fad, voluptuary and down-to-earth products are rather popular.
Nice article, thoughtful and thought-provoking. Centralised and hierarchical (Chinese/communist) organisation and apparatus always wins against the bumbling, sometimes-corrupt, Indian system. Even with similar-order-of-magnitude finance, timescales and geo-politics. Would you agree sir?