India spends 2.35 per cent of GDP on defence. This includes defence pensions; and pensions must be included because it is after all an integral part of defence expenditure. This is also the norm internationally. Therefore, it is this figure that we must use when we compare India’s defence spending with that of other countries. Coincidentally, the Indian budget in its annual statement of accounts does not include defence pensions as part of Defence Services expenditure (major heads 2076 to 2080), but as part of Pensions and Other Retirement Benefits (major head 2071). This could explain why most defence analysts prefer to quote India’s defence spend at 1.7 per cent, which of course excludes pensions.
There have been repeated demands for defence expenditure to be increased to 3 per cent. This is a tall ask for India. India’s current defence expenditure excluding pensions (INR 2,62,390 crores) is greater than the entire subsidy bill for food, fertiliser and petroleum (INR 2,40,339 crores) by 8 per cent. The difference alone, which is INR 22,051 crores, is enough to fund Commerce and Industry or External Affairs or IT and Telecom.
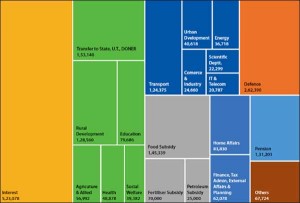 It is reckless to have a target figure that is completely disconnected from defence procurement plans for the future. Few may know, that defence already receives 16 per cent of the Union Budget, second only to interest payments. Defence is the single largest recipient of budget allocation as a stand-alone sector. The highest has been approximately 17 per cent (refer Table 1). This should lay to rest the oft-repeated complaint that the defence budget allocation is not a priority, but it will not.
It is reckless to have a target figure that is completely disconnected from defence procurement plans for the future. Few may know, that defence already receives 16 per cent of the Union Budget, second only to interest payments. Defence is the single largest recipient of budget allocation as a stand-alone sector. The highest has been approximately 17 per cent (refer Table 1). This should lay to rest the oft-repeated complaint that the defence budget allocation is not a priority, but it will not.
|
Table 1: Percentage Share of Expenditure on Major Items from Union Budget[2] |
||||
| Major Item |
2015-16 |
2016-17 |
2017-18 BE) |
|
| 1 | Defence |
16.41 |
17.13 |
16.76 |
| 2 | Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution (includes Food Subsidy) |
7.86 |
7.15 |
7.18 |
| 3 | Rural Development |
4.41 |
4.85 |
5.02 |
| 4 | Human Resource Development (Education) |
3.75 |
3.65 |
3.71 |
| 5 | Road Transport and Highways |
2.62 |
2.60 |
3.02 |
| 6 | Agriculture, Cooperation and Farmer Welfare |
1.23 |
2.39 |
2.38 |
| 7 | Health and Family Welfare |
1.97 |
2.04 |
2.34 |
The holy three per cent demand has never been backed by reasoning. Defence establishment and analysts should explain how the holy figure of 3 per cent was arrived at? What justifies the 3 per cent figure? More importantly, it should be clarified whether the 3 per cent is inclusive or exclusive of defence pensions, which forms a sizeable portion of expenditure. At 3 per cent of GDP the defence spend, based on our current GDP figures would amount to an allocation of INR 4,57,531 crores. If 3 per cent is not the sacrosanct figure, we assume that it is the monetary equivalent that is sacrosanct. It is assumed that this is the amount required to meet our defence needs, and that this figure is linked to the modernisation and integrated plans for procurement. The difference between our current spend on defence including pensions (INR 3,59,854 crores) and the figure for 3 per cent of GDP (INR 4,57,351 crores) is INR 97,677 crores.
The aim of this piece however is not to examine the merits of asking for a 3 per cent spend or its monetary equivalent spend on defence even though the authors are of the opinion that a higher defence spend does not guarantee a fully equipped force. On the other hand this piece will take the above demands on their merit and go a step further and assume that the there is a genuine need for these monies for fair allocation amongst all armed forces. Under these assumptions the question really is on how to raise the money to meet the monetary obligations for defence. India has a few options before her.
Option one is to make up the difference by reallocating monies from other sectors. In a country like India, the government also has a responsibility towards its people in providing access to healthcare and education. Over the last five years, there has been a declining trend in public expenditure in the social sectors. India cannot afford to divert money from priority development sectors into defence, especially since the majority of it funds an import bill rather than in developing our domestic industrial base.
|
Table 2: Defence Budget – Current and Projections[3] |
|||||
|
(in INR crores) |
2017 |
2020 Growth Projections |
|||
|
at 7% |
at 8% |
at 9% |
at 10% |
||
| Current GDP |
15251028 |
18683165 |
19211903 |
19750524 |
20299118 |
| Defence Spend (excl. pensions) (1.7% of gdp) |
274114 |
335801 |
345305 |
354986 |
364846 |
| Defence Spend (incl. pensions) (2.3% of GDP) |
359854 |
440837 |
453312 |
466021 |
478966 |
| Defence Spend at 3% of GDP |
457531 |
560495 |
576357 |
592516 |
608974 |
Option two is to increase GDP growth to meet the monetary target of INR 4,57,351 crores assuming that the percentage of GDP spend remains constant at 2.35 per cent. Table 2 presents four scenarios of growth for India up to 2020. The only way that India can meet her monetary target for defence spend is if India continues to grow at a rate between 8-9 per cent year on year. At a more realistic growth rate of 7 per cent the budget allocation for 2018 would be INR 3,83,487 crores. This would mean a deficit of approximately INR 74,000 crores.
Option three, is to ignore fiscal prudence and opt for deficit financing of defence, that is, either borrow money or print money to finance India’s defence expenses. Financing a deficit of INR 1,06,070 crores in 2018 (the difference between a 2.35 per cent of GDP and a 3 per cent of GDP spend) will increase India’s fiscal deficit by 0.65 per cent. Financing a deficit of INR 2,00,641 crores, to meet the target of INR 5,60,495 crores which is 3 per cent of GDP (Table 2), in 2020 will mean doubling the fiscal deficit to 1.07 per cent. India has only just managed to rein in fiscal deficit to 3 per cent by practicing great fiscal prudence. It is neither advisable nor affordable for India to increase the defence budget allocation at the cost of compromising the country’s fiscal goals.
Option four, fiscally speaking, is the most feasible. The INR 1 lakh crore gap can be met by levying a defence cess. The primary education cess (2 per cent) brought in INR 99,352 crores from 2010-2015 and the Clean Energy cess (0.5 per cent) has brought in INR 15,174 crores since 2010. The Swachh Bharat Cess (0.5 per cent) which has been levied since November 2015 brought in INR 3,902 crores in the last quarter of 2015-16.[4] In order to cover even a fraction of the desired allocation for defence by 2020, a defence cess of at least 3 to 4 per cent would have to be levied. The total difference of INR 1 lakh crores can only be covered with an annual defence cess of 5 per cent. Such a cess will drive up indirect taxes. However, the acceptance of a defence cess is unlikely. That such a cess would be easily accepted even by the armed forces is unlikely.
Apart from levying an undesirable defence cess, India has no other feasible options to fulfil the demand for an increased defence spend. This puts into perspective the very harsh realities of the monetary, the administrative and the allocation challenges to increasing defence budget.
Defence is generally a cost centre for any government, and India is no exception. Countries like Russia, Israel and the United States, which have sizeable arms exports, generate significant returns on defence investments. This is something that the defence establishment in India would do well to keep in mind. Table 3 gives the ratio of the amount earned by nations through arms exports to the amount of their military expenditure. Russia, whose economy is driven in large part by their arms industry, earns more out of defence than they spend, i.e. USD 1016 earned for every USD 1000 spent on defence. Israel and the United States both earn some revenue from their arms exports, which helps fund part of their defence spending. It is however interesting to note that China which was until a couple of decades ago a net importer of arms, now earns significant revenue from its arms exports.
Table 3. Ratio of Arms Exports to Military Expenditure[5]
| Country |
Ratio of Arms Exports to Military Expenditure (million USD) |
| Russia |
1016 : 1000 |
| Israel |
315 : 1000 |
| United States of America |
124 : 1000 |
| China |
75 : 1000 |
| India |
4.5 : 1000 |
| Pakistan |
3.7 : 1000 |
Compared to these nations India spends a significant amount on defence with nothing to show by way of arms revenue, exports or otherwise. For India, spending USD 1000 on defence earns a measly USD 5 from arms exports. This has perhaps been the driving force behind India’s increasing focus on domestic defence production and defence exports, be it through the Make in India policy or through the Defence Procurement Policy (2016), to name a few.
Table 4: India’s Defence Exports[6]
|
2012-13 |
2013-14 |
2014-15 |
2015-16 |
upto Dec 2016 |
|
| Defence Exports Value(in INR crore) |
460.97 |
686.27 |
994.04 |
2059.18 |
1105.2 |
| Defence Exports(as % of GDP) |
0.005 |
0.006 |
0.008 |
0.015 |
0.007 |
Strategic interests dictate that it is crucial that the requirements of the armed forces are fulfilled. After all, our forces cannot protect our borders whilst ill-equipped and ill-disposed. Short term import dependency for strategic equipment and arms can be understood; but India has made little progress in reducing this dependency. It is common perception that the inability of the domestic defence manufacturers (public and private) to fulfil the requirements of the armed forces has driven India’s dependence on imports. Establishing a strong domestic defence manufacturing base and gradually increasing defence exports are the only sure path towards decreasing our import dependence and increasing revenue from defence production. If we choose to focus on sound economic decision-making and strengthening the domestic defence industrial base, the defence establishment can make a contribution to the nation’s GDP.
Budgeting, planning and prioritizing for short and medium term requirements is the need of the hour. The defence budget demands should be linked to one of the many planning documents such as the Long Term Integrated Perspective Plan (LTIPP), the Services Capital Acquisition Plans (SCAP) and Annual Acquisition Plans (AAP), both of which flow from the LTIPP and/or the Technology Perspective and Capability Roadmap (TPCR).
Budgeting, according to procurement plans that also factor in contingencies, is a specialized skill set. Ministry of Defence (MoD) would do well to revisit their entire planning and budgeting processes especially given the large gaps between budget expectations and allocations. The existing process assesses what percentage of allocation goes to each department and service. Clearly this is inadequate. There should be a central, independent department under the MoD that is dedicated to the task of preparing a comprehensive defence budget; one that is based on procurement plans, that has taken the time and effort to coordinate between the various services and brings efficiency and accountability to the process. An independent budget division is de rigueur because defence is the single largest consumer of public expenditure.
Defence analysts should remember that the pie is finite and that resources have to be shared by all sectors equitably. Wish lists should not be confused with planned procurement and budgeting should be based on the latter and not the former. If India indeed wants to move towards a 3 per cent defence spend, because that is what planned procurement demands, then it is imperative for the domestic defence industry to increase their revenue contribution to defence production. This means all defence establishments and defence manufacturing units including the MSMEs have to work together and not against each other. This is the first thing about India’s defence procurement that needs to change.
References
[1] Budget at a Glance, Union Budget 2017-18, www.indiabudget.gov.in
[2] Expenditure Budget, Government of India (various years), www.indiabudget.gov.in
[3] Union Budget, various years and Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
[4] ‘Govt collected Rs 3,902 cr Swachh Bharat cess in FY 2016: MoS Finance Santosh Gangwar’,
The Indian Express, 26th July 2016.
http://indianexpress.com/article/india/india-news-india/govt-collected-rs-3902-
cr-swachh-bharat-cess-in-fy-2016-mos-finance-2936686/
[5] SIPRI and World Development Indicators, World Bank.
[6] Annual Reports, Ministry of Defence.
Courtesy: First published on www.claws.in





I will give some more interesting figures about defence spending. India is not going to attack any country to use their natural resources. Our main enemy is Pakistan. In 1971 war India fought two fronts. For any calculations, 1971 should be the base. particularly for Airforce and the Navy. In the 1971 war, IAF was able to achieve air superiority in the East and West. They used 408 fighter planes. Out of 408 planes 240 planes used on the Western side and 168 in the Eastern side. Now there is no East Pakistan. Now they have 583 fighter planes, But they want 756 planes. The right way to calculate the requirement is to calculate the number sorties conducted to achieve air superiority. In the western side, iAF conducted 4000 sorties On those days two fighter planes were used to conduct sorties. Now single fighter plane can conduct sorties with the help of GPS or AWACs. The number of sorties will come down in future particularly against Pakistan because Majority of Pakistan Army and PAF installations are within striking distance of our missiles. The IAF and Navy are competing for each other to get number two position.
Navy’s condition
In 1971 war Govt did not give much importance. to Navy. This evident from the report is given below: – In 1971, when the three service chiefs would meet the prime minister (Indira Gandhi), she would ask the army chief first, then the air force chief, about their views on the situation. And then she would look at her watch and say, ‘Admiral, you have anything to say?’
And I’d say ‘No ma’am, I have nothing to say.’
But inside I was thinking that you can write off the navy if does not take part. That was not acceptable to me. So I had made up my mind that if there was war, the Navy would take part.
To-day Indian Navy is the 4th naval power in the world and bigger than the UK. Billions of dollars were spent on Navy but could not save the country from terrorist attack. through sea.,
Last seven years I am studying the defence requirements of and war strategy. India can’t become a developed nation so long the country spend billions of dollars to purchase unwanted defence equipment. for Navy and Air force. The South Korea, Japan and UAE all become developed nation because they spend very less amount on defence and concentrated on the high-value mercantile product. and electronic goods For Japan and South Korea their main income is from LNG vessels. and other ocean-going vessels. To-day LNG vessel is the most lucrative business in the world. But though India has got capability the Indian Govt not produced a single vessel. Instead of entering this lucrative business they decided to develop and manufacture the white elephant Aircraft carrier. Every shipyard was used to manufacture Naval vessels. At the same time they Indian Govt never tried to sell a few ships to get some income. They Navy officer and iAF officer do not know what is the real requirement. The Navy officers do not know the strategic points in the Indian Ocean. They pressurised the to purchase second-hand Aircraft carrier from UK and Russia. India becomes bankrupt. in 1990 because of unwanted purchase of Submarines, Aircraft carrier and the helicopter during Rajiv Gandhi’s period. The first Aircraft carrier purchased during Nehru’s was useless during 1965 and 1971. And it was proved beyond doubt that India does not require Aircraft carrier. I have no practical experience in the Army. Airforce, and Navy. But I have the aptitude to solve technical and Managerial problems. The 21st century is the age of missiles and rockets. The cost of SU.30 Mki is 50 to 55 million dollars. Su-30 Mki life cycle maintenance cost is 5 billion dollars.The cost of Agni-II is 5.4 million dollars. No maintenance cost. No runway or hangars required. Thousands can be manufactured every year and can be kept in Silo. So Govt should reduce the defence budget. The Present Govt knows this.
Half your stuff is nonsense. Moreover, aircraft are needed for offensive operations. If you aren’t an expert, you have to learn a lot more before you solve technological problems. Better luck next time.
Can you prove that Missiles cannot be used as an offensive weapon? Do not write comments like a layman. or a politician.
Very good article. But, the authors don’t realize that the size of the pie is NOT fixed. Therein lies the first fallacy of their hypothesis.