Evolution of the radio/radar/TV/laser brought in a domain of warfare called the Electronic Warfare (EW). This invisible silent ‘Killer’ was meant to degrade the enemy sensors and weapons. This military action to control the electronic spectrum for own use and to deny free use to the enemy became a game changer. Directed Energy (DE) is an umbrella term covering technologies that relate to the production of a beam of concentrated electromagnetic energy or atomic or sub-atomic particles. Electronic Counter Measures (ECM) involves the use of Electro-Magnetic (EM) energy to jam or deceive enemy systems and direct energy as a weapon against personnel and equipment. Electronic Counter Counter Measures (ECCM) are the passive or active means used to protect own systems from degradation by the enemy. Electronic Support Measures (ESM) involve intercepting, identifying and localising sources of enemy-radiated EM energy for avoiding, targeting and planning other future warfare actions.
Airborne systems, though limited by size and power output, have the advantage of range and reach…
“All warfare is based on deception. Hence, when we are able to attack, we must seem unable; when using our forces, we must appear inactive; when we are near, we must make the enemy believe we are far away; when far away, we must make him believe we are near”, said ‘Art of War’ scholar and Chinese General Sun Tzu in 500 BC. For centuries, the audio-visual impact of hard-kill kinetic weapons has left an indelible impact on minds of the masses. The pictures of the atom bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki and the video from the weapon-head of laser-guided missiles fired in Iraq are embedded in our minds.
Evolution of the radio/radar/TV/laser brought in a domain of warfare called the Electronic Warfare (EW). This invisible silent ‘Killer’ was meant to degrade the enemy sensors and weapons. This military action to control the electronic spectrum for own use and to deny free use to the enemy became a game changer. Directed Energy (DE) is an umbrella term covering technologies that relate to the production of a beam of concentrated electro-magnetic energy or atomic or sub-atomic particles. Electronic Counter Measures (ECM) involves the use of Electro-Magnetic (EM) energy to jam or deceive enemy systems and direct energy as a weapon against personnel and equipment. Electronic Counter Counter Measures (ECCM) are the passive or active means used to protect own systems from degradation by the enemy. The Electronic Support Measures (ESM) involve intercepting, identifying and localising sources of enemy-radiated EM energy for avoiding, targeting and planning other future warfare actions.
More recently, terms such as Electronic Attack (EA), Electronic Defence (ED), and Electronic Support (ES) have been introduced. EW goes beyond just radio or radar frequencies and includes IR, visible, ultraviolet, and other less used portions of the EM spectrum. Real EW action began in World War II when significant EM spectrum usage began. The Bekka Valley operation in 1982 demonstrated that the result of a war could greatly be decided by EW. More recently in Iraq and Afghanistan, EW has played a significant role. EW can be applied from the air, sea, land and space using manned or unmanned systems. New threats and technologies are giving rise to concepts such as spectrum warfare that seek to blend electronic warfare, cyber warfare and other technological approaches to controlling the RF spectrum. Airborne systems, though limited by size and power output, have the advantage of range and reach, and thus have greater impact.
Modern Armies have portable computing and internet capabilities on the move and could be susceptible to jamming…
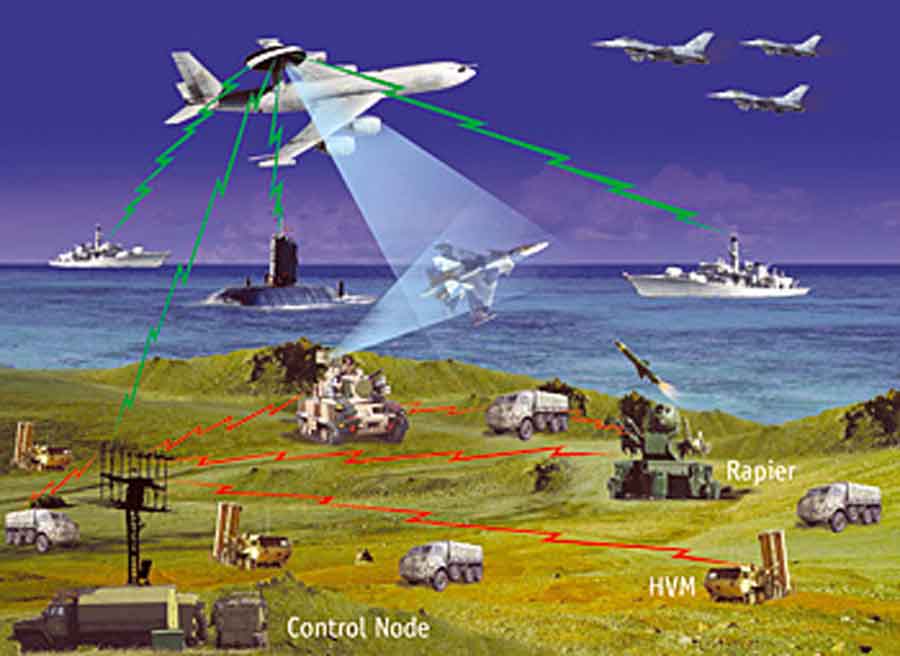
Typical Airborne EW Unit
Some of the basic EW elements required in all modern aircraft include a Radar Warning Receiver (RWR), Chaff and Flare Cartridges to act as decoys against enemy radars and IR missiles and an Airborne Self Protection Jammer (ASPJ). Dedicated EW mission aircraft would have more powerful offensive jammers, ELINT and/or SIGINT systems and Communication Jammers. All electronic systems onboard have to have inbuilt ECCM features to survive an EW attack. EW being a specialised field requiring additional technical knowledge, each unit has specially trained crew for developing tactics and programming systems.
EW Shapes Operation Outcome
Two operations spread over time zones best signify primacy of EW. During the Normandy Landings in WW II, the Germans had a radar station every ten miles on the French coast. On the night preceding D-day, deception jammers carried on eight Sterling aircraft and four B-17s were used by the British to drop chaff and dummy parachutists in the Dover-Calais area. In response, German fighters spent most of the night circling over Calais area. As a result, no fighter attacked the 884 transports and 105 gliders which landed or dropped some 15,000 troops. During the Cold War, radars became more powerful and agile, command and control networks became more resilient. Surface-to-Air Missiles (SAM) became a common inventory.
Operation Mole Cricket 19 was a Suppression of Enemy Air Defences (SEAD) launched by the Israeli Air Force against Syrian targets on June 09, 1982, at the beginning of the Lebanon war. They successfully destroyed a Soviet-built SAM network. This decisive Israeli victory is referred to as the “Bekka Valley” operation. Israeli EC-135s were initially used to obtain the location and frequency of the Syrian radars. The Israeli Air Force used ECM pods, chaff rockets, chaff from drones and stand-off jammers onboard Boeing 707 and Arava STOL transport aircraft and Sikorsky CH-53 helicopters. In the 1980s, US President Reagan proposed the Strategic Defence Initiative (SDI), also called the Star Wars which envisaged space-based X-Ray Lasers that could destroy ICBMs in flight. It is claimed that the USSR made use of the lasers at the Terra-3 site to target the Space Shuttle Challenger in 1984.
The LCA will be fitted with unified radar warning and jamming system…
The Gulf War demonstrated the real importance of EW in modern warfare. Initially, US Army AH-64 Apache helicopters crossed the Saudi Arabia-Iraq border to attack two Iraqi early warning radars. This opened the door for attacks across Iraq by stealthy F-117A flying precision strikes against important C3 nodes, radar and SAM sites. EW aircraft F-4G Wild Weasel of USAF and EA-6B Prowlers, A-7Es and A-6Es of the US Navy jammed radars while F-16C and F/A-18C used HARM anti-radiation missiles for hard-kill. Also employed were ALARM-equipped Tornado GR1s of the RAF, USAF EC-111A ravens as support jammers and EC-130 H for communication jamming. The Iraqi integrated air defence system collapsed within hours.
State-of-the-Art EW Systems
The Northrop Grumman EA-6B Prowler is capable of carrying up to five AN/ALQ-99 tactical jamming external pods; AN/ALE-43 Bulk Chaff Dispensing pod or four anti-radiation missiles such as AGM-88 HARM. It also carries a communications jamming system. Since 1998, when the USAF EF-111 Raven retired, EA-6B was the lone work horse till EA-18G Growler joined the US Navy in 2009. EA-6Bs were withdrawn in June 2016 after 40 years of service with the US Navy. US Marines will fly them till 2019. Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightening II is also being considered for EW role. Marine Air-Ground Task Force Electronic Warfare (MAGTF-EW) concept envisages medium to high-altitude long-endurance Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) to take on some of the EW missions.
The Boeing RC-135V/W equipped with Raytheon SIGINT/ELINT system is the most significant platform in USAF. The most potent support jamming aircraft are the EA-6B, EF-111A and EC-130 Compass Call. Modern tactical aircraft carry internal self-protection jammers and internal warning receivers. The Westinghouse ALQ-131(V) is the USAF’s standard jamming pod with an array of jammer modules and can be slaved to the aircraft’s RWR. Newer Raytheon ALQ-184(V) employs Rotman lens antennas and provides noise and deception jamming modes. Raytheon is also working on the US Navy’s Next-Generation Jammer (NGJ) comprising self-protection, communications, advanced EW and airborne information operations. Northrop Grumman’s new RWR and EW management system APR-39D (V) 2 merges the capability of previous systems with the digital receiver technology and provides advanced capability. Northrop Grumman is also scheduled to fit US Navy’s MQ-8C Fire Scout rotary UAV with a new external Multi-Capability EW Pod. BAE Systems is leveraging advances in signals processing in a DARPA-funded programme called ‘Adaptive Radar Countermeasures’ to tackle emerging radar threats and to countering never-before-seen threats.
Raytheon is also working on the US Navy’s Next-Generation Jammer (NGJ)…
The Next Generation Jammer is being developed to replace the current AN/ALQ-99 on the Boeing E/A-18 Growler by around 2020. It will use a small AESA antenna and retain the capability of highly directional jamming. DARPA’s Precision Electronic Warfare (PREW) project aims to develop a low-cost system capable of synchronising several airborne jamming pods with precision to avoid collateral jamming of non-targeted receivers. An expendable active decoy that uses DFRM technology to jam RF based threats has already been developed by SELEX ES. Named Brite Cloud, it is self-contained in a small canister that is similar to a standard flare cartridge. Other dedicated ECM aircraft around the world are Russian Su-24 MP, Yak-28 PP and Mi-8 PP and Chinese GX-11 based on Y-9 transport aircraft. AWACS, Boeing E-3 sentry and Boeing E-4 are the ESM aircraft.
Changing Military Environment
In the recent past, EW took on new dimensions when electronic means began being used to detonate Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs). Modern Armies have portable computing and internet capabilities on the move and could be susceptible to jamming. It is time for armies to integrate Cyber and Signal capabilities into EW. Till now, the Air Forces and Navies had most of the EW capability. Aircraft carriers have complexities of massive number of high powered radars, antennas, and other electronic systems operating simultaneously in a dense shipboard EM environment and have also to cater to sub-surface threats. Air Forces have to cater to very confined aircraft space and need to compensate high speed motion. Tri-Services Cyber/EW Coordination is another important activity to avoid EW fratricide.
Modern EW Suite
Unlike the previous generation of fighters, the F-35 was designed for very-low-observable characteristics. Besides radar stealth measures, the F-35 incorporates IR signature and visual signature reduction measures. The F-35 must fly most missions without external tanks. Unlike the F-16 and F/A-18, the F-35 lacks leading edge extensions and instead uses stealth-friendly chines for vortex lift. These inlets improve the aircraft’s very-low-observable characteristics. Additionally, the “bump” surface reduces the engine’s exposure to radar, significantly reducing a strong source of radar reflection. The Y-duct type air intake ramps also help in reducing RCS, because the intakes run parallel and not directly into the engine fans. The EW-friendly suite of the F-35 includes, the Northrop Grumman AN/APS-81 AESA radar, Lockheed Martin AAQ-40 electro-Optical Targeting System (EOTS), AN/AAQ-37 Distributive Aperture (DAS) missile warning system and BAE Systems EW System. DAS consists of six high resolution IR sensors to provide unobstructed spherical coverage around the aircraft. The DAS provides three basic functions in every direction; missile detection and tracking; aircraft detection and tracking; and situational awareness based air-to-air weapons cueing. DAS has demonstrated the ability to detect and track ballistic missiles to ranges exceeding 1,300 kilometres and has also demonstrated the ability to detect and track multiple small suborbital rockets simultaneously in flight.
Airborne EW Action IAF
The IAF formed its first dedicated EW Squadron equipping No 35 Squadron with Canberras and MiG-21 aircraft with stand-off and escort jammers respectively. Jaguars were the next to get the ‘Dawn’ podded jammer. With the Mirage-2000 came the first dedicated EW suite that included the Thales Serval internal RWR, internal ABD-2000 ASPJ, Remora podded ASPJ, Caiman Escort jammer and the Syrel ELINT pod. SU-30 MKI too has a comprehensive EW suite that includes OLS-30 laser-optical IRST with day-and-night FLIR capability which enables engagement of the target even when partly obscured by clouds or countermeasures; the Tarang RWR developed by DRDO and the Elta EL/M-8222 self-protection jammer developed by Israel Aircraft Industries with an ESM receiver integrated into the pod.
DAS has demonstrated the ability to detect and track ballistic missiles to ranges exceeding 1,300 kilometres…
India’s DRDO labs are working on a host of EW Systems for application on airborne, space-based and surface systems. Most indigenous EW systems developed by DRDO included Dawn, Tempest, Tarang, CMDS, Samyukta, COIN for various fighter aircraft such as MIG 21, MIG 23, MIG 27 Jaguar, Su-30, Sea Harrier and LCA had limited success. Bharat Electricals Limited (BEL) produces most indigenous EW systems. MiG-29 and Su-30 MKI need upgrade of their EW suite. EW suite of Light Combat Aircraft Tejas and Light Attack Helicopter (LAH) are still evolving. DRDO’s Defence Avionics Research Establishment (DARE) EW suite completed first flight on Tejas-PV1 LCA early 2015.
The LCA will be fitted with unified radar warning and jamming system. The flight testing will take some time for the system to become operational. India’s Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) Dhruv is equipped with a Swedish Saab EW suite. The Rafale will bring new EW technologies. It features an integrated system named SPECTRA developed jointly between Thales and MBDA, which protects the aircraft against airborne and ground threats. SPECTRA would allow Rafale to become independent of SEAD platforms. The effective radiated power (ERP) of the EL/M-2080 Green Pine radar, with India, makes it a possible candidate for conversion into a directed-energy weapon, by focusing pulses of radar energy on target missiles.
Indigenous EW Projects
DRDO’s Brazilian Embraer EMB-145 aircraft was chosen as the AEW&C platform and three aircraft purchased for $210 million. The first aircraft arrived on August 16, 2012. The IAF needs 24 such platforms. The aircraft will have Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) primary radar. The system will also have Electronic Support Measures (ESM) and Communications Support Measures (CSM) ability. There will be datalinks to network with the fighters, and ground-based control systems. Aircraft’s Self Protection Suite will have a passive Missile Approach Warning System, a Radar Warning Receiver and countermeasures dispensers. The DRDO and the Bengaluru-based Centre for Air Borne Systems (CABS) have also launched a new project to build larger and more capable AWACS. Initially, two AWACS aircraft will be developed, with four more to follow at a later stage. Clearances for the project were received from the government in January 2013.
There is a high probability that terrorist and criminal groups may possess Man Portable Air Defence Systems (MANPADs)…
In 2014, the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) finally approved `1,100 crore for the IAF’s long awaited nine ‘Special Mission’ aircraft. These multi-mission aircraft with Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), aerial survey, target towing, and Communication Jamming (COMJAM) militarised business jets would replace the retired Canberra and Avro aircraft. This acquisition would meet airborne special-mission requirements currently serviced by a small fleet of Gulfstream III SRA ELINT jets operated by the country’s external intelligence agency, R&AW. Embraer and IAI may be the main contenders. Embraer would pitch for advantage of commonality with DRDO AEW&C and IAI may offer more affordable Gulfstream G200/280 which it manufactures under license in Israel. US Hawker Beechcraft with Raytheon L-3 communications and Lockheed Martin or Boeing systems could also be in the race. The IAF is also looking for systems that merge cyber and EW techniques akin to US next generation jammer. Israeli Elbit Systems EW and SIGINT Company ‘Elisra’which provides comprehensive solutions in the electromagnetic spectrum domain is working closely with BEL and Private sector Samtel Group for aircraft EW systems. All aircraft have to be capable of operating from airfields located up to an altitude of 10,000 ft such as Leh and Thoise.
India’s Indigenous Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) developed by DRDO’s Electronics & Radar Development Establishment (LRDE) for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) is reportedly progressing well and may be flight tested by early 2017 on a modified Dornier Do-228. LRDE’s SAR is planned to be integrated with India’s Rustom-2 which is Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) UAVs at later stages. LRDE is also planning to develop a derivate of this radar for operations from manned reconnaissance aircraft including a maritime variant. L&T CASSIDIAN Ltd is working on Tactical Radar for Ground Surveillance (TRGS) system that utilises AESA technology for ground surveillance missions.
Samyukta is an ambitious mobile integrated EW system developed jointly by DRDO, BEL, ECIL and Corps of Signals of the Indian Army that includes ELINT, COMINT and electronic attack. The Indian tri-services Defence Communication Network (DCN) would give ‘jointness’ to connectivity and will be the backbone of the proposed joint commands for cyber warfare, Special Operations and space operations.
China is developing anti-laser defences because protection against them is considered far cheaper than creating competing laser weapons…
EW Against Militants
There is a high probability that terrorist and criminal groups may possess Man Portable Air Defence Systems (MANPADs) and other IR/electro-optical systems. The employment of flares and IR jammers may become an operational requirement to counter these threats during peacetime missions even on friendly soil. EM weapons can also be used against militants. Active Denial systems use a millimetre wave source that heats the water in the target’s skin and thus causes incapacitating pain is good for riot-control duty. Though intended to cause severe pain, it leaves no lasting damage. IED and mobile link jammers are already being used extensively. In 2015, Lockheed Martin reported a demonstration of the ATHENA Laser Weapons System that disabled the engine of a truck from a distance of one mile.
World EW Market
The World EW market was valued at $17.72 billion in 2014 and is expected to grow to $24.25 billion by 2020. The emerging nations such as India, Japan, China, Israel and Saudi Arabia among others are expected to have high growth potential in EW. $4.0 billion EW business awaits takers in India. The key market players includes Raytheon (US), Alliant Techsystems Inc. (US), BAE Systems (UK), Rockwell Collins (US), IAI Elta (Israel) and L-3 communications (US), General Dynamics Corporation (US), SAAB (Sweden), Thales (France) and Teledyne Defence Ltd (UK). Increasing use of EW systems in unmanned vehicles, use of EW in commercial aviation are some of the major opportunities accelerating the growth of EW market. China is developing anti-laser defences because protection against them is considered far cheaper than creating competing laser weapons themselves.
The Future
An advanced digital EW architecture for the next-generation support jammer called ICAP-3 is becoming operational in USA. Initially deployed on EA-6B Prowlers it is now transiting to more modern aircraft. The US House of Representatives have established an Electronic Warfare Working Group conceived to assure greater congressional understanding and oversight of electronic-warfare systems and missions. For the US to maintain its military edge, it needs to control the electromagnetic spectrum. Integrating the current forest of antennas onboard a ship into a single shared multi-function, multi-beam aperture array covering a wide range of frequencies is under evolution. Improvement in microprocessors and solid state gallium nitride amplifiers are on the cards. Photonics for very wide bandwidth and high dynamic range are next.
With India already becoming a critical peg in the Asia-Pacific region, access to more technologies would be available…
General Atomics Predator class UAVs may be used for Electronic Attack or Support in the future. The Reaper using the Northrop Grumman’s new Pandora EW system could advance its existing ISR role to a broader spectrum of EW missions. USAF announcement in 2014 a requirement for the Advanced Novel Spectrum Warfare Environment Research (ANSWER) programme to develop advanced computing, signals processing, anti-tamper and software protection technologies, GPS alternatives, visual and laser-based navigation and electro-optics countermeasures. The move to use F-35 as the new EW platform may be difficult to justify as an expense vis-à-vis the Growler. The future will see unmanned systems doing more EW, whether that is a single platform or a flock of UAVs doing jamming.
Modern Directed-Energy Weapons (DEW) systems emit highly focused energy to damage the target. DEW include anti-personnel weapons, attacking missile defence system and disabling lightly armoured vehicles such as cars, drones, watercraft and electronic devices such as mobile phones. Energy used could be EM radiation covering radio frequencies, microwave, lasers or masers. Particle-beam weapons and sonic weapons are also used. Some of these systems offer advantages of pin-point accuracy at the speed of light. They are discreet and can travel very long distances without effect of gravity or atmospherics. Energy can be targeted simultaneously at multiple targets from the same mother source. USA is researching DEW to counter threats posed by missiles and hypersonic glide vehicles. Some these are expected to mature by mid-2020s.
Early August 2016, it was reported that Russian laser weapons have started entering service. The US Navy is already deploying laser weapons aboard ships and combat aircraft will be the next receiving them. Electronic warfare is intimately tied to advances in technology. With the possible drawdown in Afghanistan and the planned Asia-Pacific Pivot, EW will enter the new contested region. USA and allied forces would face near-peer, anti-access or area denial environment and a greater emphasis on the air-sea battle. With India already becoming a critical peg in the Asia-Pacific region, access to more technologies would be available. The EW Domain is all set for greater action.